FHA Compensating Factors For Manual Underwriting
When are Lenders Requiring Compensating Factors to obtain FHA Loan? Compensating factors are positive factors normally required on manual underwrites or borrowers with marginal credit and/or higher debt-to-income ratios. For manual underwrites with higher debt-to-income ratios, compensating factors are required. Compensating factors give strength to borrowers when underwriters evaluate the applicant’s mortgage file. Borrowers who cannot get an automated approval by the Automated Underwriting System, also known as AUS, may qualify via manual underwrite with refer/eligible automated findings where the mortgage application is manually underwritten.
Compensating factors are elements in a borrower’s loan profile that may offset certain risk factors. These often include strong employment history, a high credit score, or a large down payment.
For borrowers with weaker profiles, these compensating factors can help to swing a loan approval in their favor. And for borrowers with strong profiles, can help to improve the terms of their loans.
In this article (Skip to…)
Many borrowers often ask the question What Are FHA Compensating Factors?
- Lenders are not required to originate and fund mortgage loans
- Just because there are home loans that are insured by the government such as FHA, VA, and USDA Loans,
- it is not a requirement for lenders to follow the minimum government lending guidelines
- Lenders can have their own overlays
- Lenders can set their own lending standards that are above and beyond those of FHA, VA, and USDA
- These additional mortgage lending guidelines are called lender overlays
In this article, we will cover and discuss What Are FHA Compensating Factors And Importance On Manual Underwriting.
FHA Compensating Factors Required For Risky Borrowers
Lenders will not fund a loan where they feel is a risky candidate:
- Low credit score borrowers may have a high probability of defaulting on their home loan
- Even though a mortgage may be insured by FHA, no lender wants to go through a borrower defaulting on their mortgage loan and having FHA insure it
- This is because HUD monitors every single defaulted FHA Loan
- If lenders have a high default rate, they can be cut off from HUD
How Compensating Factors Help Higher Risk Loans
What Are FHA Compensating Factors?
- Compensating Factors are positive factors that a borrower has that will strengthen the borrower’s credit profile
Mortgage Underwriters look for strong FHA compensating factors on borrowers who have a higher layer of risk such as the following:
- Low credit scores
- No established credit
- Borrowers who live with family and have no verification of rent
- Those who have large amounts of outstanding collection accounts
- Buyers with higher debt-to-income ratios
- Folks with gaps in employment and short term on the job or industry
- Homebuyers who do not have their own funds for the down payment and closing costs and are depending for gift funds
- Consumers with other credit or financial issues that pose a higher risk level
FHA Compensating Factors On Home Loans
FHA Loans is by far the most popular loan program in the United States today. Borrowers with the following can qualify for FHA Home Loans:
- bruised credit
- prior bankruptcies
- foreclosures
- deed in lieu
- short sale
- outstanding collection accounts
- charge off accounts
- higher debt to income ratios
- recent late payments
- no or little credit tradelines can often qualify for FHA Loan
But depending on their credit profile, compensating factors may be required for them to get mortgage approval.
- FHA lenient mortgage lending guidelines make it possible for many hard-working Americans to qualify for an FHA Loan
- But yet, lenders are very careful on who they lend
- This is because the last thing they want is for the borrower to default on their FHA Loan and go into foreclosure
HUD Guidelines On Home Purchase Loans
Below are the FHA Guidelines to qualify for an FHA Loan:
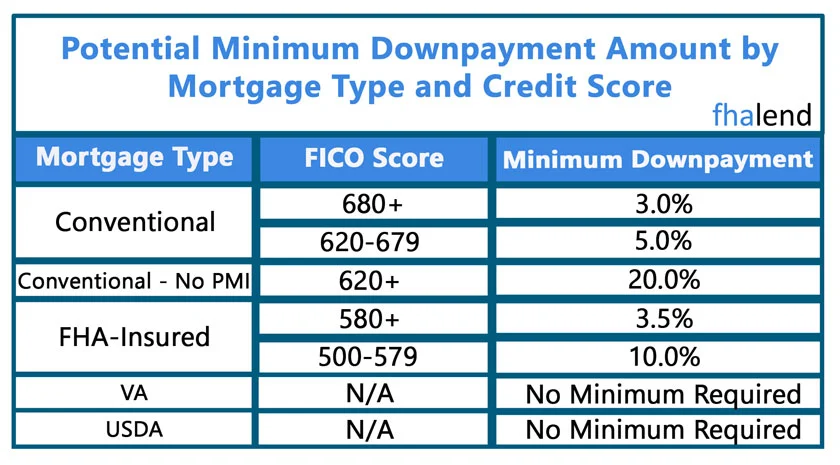
- The minimum credit scores to qualify for a 3.5% down payment FHA Loan is 580 FICO
- HUD does not require borrowers to pay off outstanding unpaid collection accounts or charge off accounts
- HUD doesn’t require borrowers to pay off judgments and/or tax liens to qualify for FHA Loans if they have a written payment agreement
- need 3 months of payment history
- need to provide three months of canceled checks
HUD Gift Funds And Non-Occupant Borrower Guidelines
HUD permits to get 100% gifted funds by a family member to be used for the down payment and closing costs:
- HUD allows borrowers to have multiple non-occupant co-borrowers
- non-occupant co-borrowers needs to be related to the borrower by blood, law, or marriage
- HUD allows debt-to-income ratios to be capped at 56.9% DTI for borrowers who have greater than 620 Credit Scores
- Borrowers with credit scores can have a maximum debt to income-ratio not greater than 43% DTI
- Borrowers who are into a Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Repayment Plan can qualify for VA and FHA Loans one year into the Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Repayment Plan
- Need approval of the Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Trustee
- Proof of 12 months of timely payments
- This is a manual underwriting
- All manual underwrites require verification of rent
- HUD has no waiting period after a Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Discharged Date
If you have several of the above conditions, FHA compensating factors will help. Compensating factors are factors that help borrowers offset the negatives on their credit and financial profiles.
Examples Of Compensating Factors
What Are FHA Compensating Factors? There are five solid compensating factors lenders like to see with high-risk mortgage loan applicants: Compensating factors will offset risks levels loan applicants has. Will help mortgage underwriters approve the file when it can be a potential denial.
Compensating Factors Mortgage Underwriters Will Take Into Consideration
Below are FHA compensating factors that lenders will take into consideration:
Verified And Sourced Reserve Funds:
- Reserve Funds cannot be gifted funds
- Reserves are above and beyond funds needed to close
- Reserves funds that are verified funds that are equal to or greater than three months of the proposed P.I.T.I. (Principal, Interest, Taxes, Interest) of the subject property
- Reserves are required on multi-unit dwelling
- Reserves are considered a strong compensating factor for the borrower
Verified and documented reserve funds that are equal to 6 months of P.I.T.I. on three to four-unit subject, purchase properties are considered strong compensating factors.
Payment Shock And Verification Of Rent
Payment Shock And Verification Of Rent :
- Lenders are often concerned with Payment Shock
- What Payment Shock is when renter go from how much they are currently paying for rent to what they will be paying on the mortgage payment
- Or the least increase they will have from paying rent to paying their new mortgage payment, the better
- What is compensating factors on payment shock?
- A great compensating factor when it comes to payment shock is if your new P.I.T.I. does not exceed 5% or $100.00, whichever amount is the lesser
- This is proven and documented by providing 12 months of canceled checks that are paid to the landlord
- Timely 12 months payments are only considered compensating factors and not late payments
On a purchase transaction, many lenders will allow one 30-day late rental payment in the past 12 months.
Borrowers With No Discretionary Monthly Debt Payments
Borrowers Do Not Have Discretionary Debt:
- Another FHA compensating factor is when there are no other debts other than the proposed housing debt
- For example, credit card debts being paid off in full monthly and no installment loans or other loans
- Credit tradelines are FHA compensating factors as well but need to be paid off in full in the past six months
Significant Additional Other Income :
- Additional other income such as overtime income, bonus income, part-time income, or seasonal employment income that is not used for income qualification purposes on the mortgage loan application
- Have been seasoned for at least one year
- Is likely to continue is considered as compensating factor
Residual Income Is Considered Compensating Factor:
- Borrowers need to have a residual income
- This includes all members of the household of the occupying Borrower without regard to the nature of their relationship
- An individual may be omitted from the “family size” if they are fully supported from a source of verified income which is not included in the effective income (must be documented)
There are many different types of compensating factors that can be considered by lenders, if you don’t have one of below you might need to provided a compensating factor to qualify for a FHA loan.
A strong employment history
Lenders want to see that borrowers have a steady income and a history of employment. This can offset risk factors such as a low credit score or a high debt-to-income ratio.
A high credit score:
A high credit score is a sign that borrowers are responsible with their money and have a good history of making payments on time. This can help to offset risk factors such as a weak employment history or a high debt-to-income ratio.
A large down payment
A large down payment shows that borrowers have skin in the game and are committed to repaying their loan. This can help to offset risk factors such as a weak employment history or a low credit score.
Compensating factors are just one element that lenders consider when determining whether or not to approve a loan. Borrowers with strong compensating factors may still be denied for a loan if they have other risk factors such as a low credit score or a high debt-to-income ratio.
If you’re considering applying for a loan, it’s important to speak with a lender to learn more about what factors will be considered in the approval process. By understanding all of the elements that go into a loan decision, you can better prepare your application and improve your chances of getting approved.
FHA AUS Approved Borrowers May Get Downgraded to Manual Underwriting

Some approve/eligible per AUS borrowers may need to be downgraded to manual underwrites; Positive factors are important on manual underwrites; Also, borrowers with very marginal credit scores or high debt to income ratios, are considered higher risk borrowers so this needs to be offset by FHA compensating factors; For example, borrowers who have poor credit, high debt to income ratios, multiple open collections, declining income, unstable jobs, multiple jobs in a short period of time, or other risk associated credit and/or financial profile on their mortgage application are considered higher risk borrowers; Positive factors need to be addressed to offset the risk; In this article, we will cover and discuss the importance of FHA compensating factors on manual underwriting.
Minimizing Risk With Positive Factors
Layers of risk from the mortgage loan applicant must be offset by Compensating Factors. Compensating Factors are strengths of borrowers. Offsetting risk factors help to demonstrate the borrower’s willingness and ability to repay the mortgage loan. These factors oftentimes can be the difference between getting a mortgage approval or a mortgage loan denial. Borrowers need to realize that all borrowers have a certain degree of risk factors. Therefore, combining these risk factors by offsetting them with FHA compensating factors will dramatically improve the chances of the mortgage loan defaulting.
Here Are Some Examples Of Borrowers With Minimal Risk Factors
Below is a list of compensating factors that can be used for high debt to income ratio borrowers:
- High residual income (average is $1,200 for a single person household and $2500 for a 2+ person household)
- Low Debt to Income Ratios which is normally 5% or more under the mortgage program guidelines.
- Long credit history with high credit scores
- Credit scores that are over 720 FICO
- Multiple aged credit tradelines
- Diversified types of credit are strong positive factors that will help borrowers.
Strong Positive Strengths Of Borrowers
For example, strong factors with credit will be having a combination of the following:
- credit card payment history
- auto loan payment history
- installment loan payment history
- personal loan payment history
- mortgage payment history
- Having different types of credit accounts versus just credit cards or just installment loans are not just viewed favorably but will also maximize credit scores
Liquid reserves of at least three months of principal, interest, taxes, and insurance are strengths for borrowers.
Ability And History To Save
The ability of borrowers to save is a strong positive factor:
- Saving patterns and saving history carry a lot of weight
- Minimum payment shock, normally 5% or less is a strong positive factor.
- For example, if a borrower has rental verification of $1,000 per month and his proposed new housing payment of principal, interest, taxes and insurance is $1,050, this is a 5% payment shock and is considered a positive favorable factor
- A larger down payment than the minimum down payment required is considered strong favorable factors
- Verifiable housing history (verified through a Property Management Firm or 12 months of bank statements/canceled checks showing a minimum of 0x30x12)
Own-sourced funds versus gift funds are considered strengths for borrowers.
Employment History And Job Stability
Employment history:
- Longevity on the current job shows and carries a lot of weight versus multiple jobs in the past two years
- Consistent pay increases and/or job promotions show stability and likelihood to remain employed with future promotions and pay increases show strength and stability
- Verified income but income that cannot be used shows strength and a great positive factor
- For example, if the borrower has held a part-time job or has overtime income for the past 18 months, this income cannot be used because the minimum required for a part-time job and/or overtime income is at least a 24-month history
This is a verifiable income but cannot be used for income qualification.
Examples Of High-Risk Factors
The following items are considered high risk by mortgage loan underwriters and are cases where Lenders Requiring Compensating Factors: Little to no cash:
- Down payment being gifted
- Having limited or no reserves
Minimal down payment and 100% gift funds for the down payment:
- Poor credit history and recent late payments
- No rental verification
- Short-term credit tradelines and limited credit
- High debt to income ratios
- Job hopping and job gaps in the past two years
- Declining income
- Irregular income
Manual Underwriting
Manual Underwriting is allowed with FHA Home Loans and VA Loans. To be eligible for manual underwriting, borrowers need timely payments in the past 12 months. Verification Of Rent is required on manual underwrites. Borrowers with less than perfect credit need to realize the importance of compensating factors. The importance of compensating factors needs to be taken seriously because it can mean whether the borrower gets a loan approval or denial.
Strength and positive factors give the mortgage applicant who has the following:
- bad credit
- high debt to income ratios
- limited credit history
- Needs to be manually underwritten to add strength when a mortgage underwriter evaluates the applicant’s mortgage application.
- The importance of compensating factors is crucial with borderline credit and challenged mortgage loan applications
- It will be the determinant of whether the mortgage loan application gets approved or not
Importance Of FHA Compensating Factors On Manual Underwriting
Those mortgage applicants who cannot get automated approval by the Automated Underwriting System may qualify through manual underwriting.
When a mortgage loan originator submits a mortgage loan application through the Automated Underwriting System, it will yield the following:
- approve/eligible
- referred/eligible
- referred with caution
A referred with caution means that the mortgage loan applicant does not qualify.
- A referred/eligible means that the mortgage loan applicant is qualified but cannot get an automated approval but is eligible for a manual underwrite
With manual underwrites and for those mortgage applicants who do get an approve/eligible with very marginal credit scores or high debt to income ratios, lenders look for compensating factors.
When FHA Compensating Factors Benefit Manual Underwriting Borrowers
Cases, where borrowers need to realize the importance of compensating factors, are when a mortgage borrower has the following:
- low credit scores
- limited credit history
- open collections with a balance
- not enough credit tradelines
- higher debt to income ratios
- Very little assets
- getting 100% gifted funds from family members for the down payment and/or closing costs
- multiple jobs in the past two years
- gaps in employment
- declining income is not positive and shows that the borrower’s file is weak
Mortgage underwriters have a lot of power and underwriter discretion on manual underwrites.
Layered Risks Of Borrowers
Depending on the number of layers of risk borrowers have, it must be offset by the substantial strengths of the borrower. The more the risk factor, the more strength, and positive factors will be needed. Borrowers need to prove that they can make their mortgage payments and need to show strength. Show the underwriter a purpose to offset the level of risk. The Importance Of Compensating Factors is to show strengths offsetting any risk factors which help to demonstrate the borrower’s probability and willingness and ability to repay the mortgage. Providing compensating factors can be the difference between getting approval and a clear to close or getting a denial. There is a certain degree of risk factor with almost every mortgage loan.
Factors That Show Strength And Considered Compensating Factors
Residual income (average is $1,200 for a single person household and $2500 for a 2+ person household)
- Long established credit history with high credit scores
- Credit scores that are over 740 are considered a good credit
- If a mortgage applicant has maintained higher credit scores year after year, it is considered strengths
- Lower DTI (Debt to Income Ratios) which is normally 5% or more under the mortgage program guidelines
- For example, if the maximum debt-to-income ratio is at 45% and the borrower has a debt-to-income ratio of 40% or lower, that would constitute a compensating factor
- Substantial credit tradelines that have been aged
- No late payment history aged
- Diversified types of credit are considered very strong factors
What’s viewed as a strong factor with credit is having a combination of credit card payment history:
- auto loan payment history
- installment loan payment history
- personal loan payment history
- mortgage payment history
Mortgage underwriters have a lot of discretion on manual underwriting. Underwriters can exceed the recommended debt-to-income ratio on manual underwriting on borrowers with multiple strong compensating factors.
Different Types Of Seasoned Credit Tradelines Are Considered Strong Compensating Factors
Variety of credit tradelines instead of just one type of credit tradelines. Having different types of credit accounts as opposed to just credit cards or just installment loans is viewed favorably and also maximizes credit scores. Liquid reserves of at least three to six months of housing payments, PITI (principal, interest, taxes, and insurance) are considered extremely strong points. The more reserves and assets borrowers have, the stronger the mortgage file.
History of Saving is Considered Compensating Factor
Lenders view the ability for borrowers to save as strong assets. The mortgage applicant’s saving patterns and saving history carry strong weight on a mortgage loan applicant who has marginal credit high debt to income ratios, or other credit issues. Minimum payment shock, normally 30% or less shows strength for borrowers. For example, if the mortgage loan applicant has rental verification of $2,000 per month and his proposed new housing payment of principal, interest, taxes, and insurance is $2,000 per month, this is a 0% payment shock and is considered a positive. A payment shock of 5% or less is considered a strong compensating factor.
Larger Down Payment Means Less Risk For The Lender
Homebuyers who have a large down payment than the minimum down payment required is considered a good factor. Provides strength. The larger down payment also poses less risk for the lender as well. Rental verification shows the history of the borrower being able to make timely housing payments. Housing payment history and proof of payment via 12 months canceled checks show housing responsibility. VOR can only be used if borrowers have been paying their housing payments with checks for the past 12 months if the home they were renting was from a private landlord. If borrowers have been paying with cash, that cannot be used as proof of housing payment even though they get rental cash receipts from the landlord.
Importance Of Compensating Factors: Examples Of Compensating Factors
FHA allows home buyers to get gift funds for their down payment and closing costs. Gift funds show weakness for the applicant because the home buyer is relying on the down payment from a family member or relative and does not have their own skin in the game. Own-sourced funds for the down payment and closing costs versus gift funds are considered compensating factors. Employment history – A long employment history shows job stability and the likelihood of future employment. Longevity on the current job carries a lot of weight versus multiple jobs and gaps in employment in the past two years.
Job Longevity and History of Raise and Promotion Considered Compensating Factor
Lenders view consistent pay increases as a strong sign of future job stability. Also, if borrowers had a history of job promotions, this too is viewed very favorably. Borrowers with a history of going to school throughout the year to better themselves and/or themselves is considered another positive sign of future job stability. Borrowers with income that cannot be used but can be verified because of not having a two-year history and/or proof that the income will continue for the next three years, will be considered a good likelihood of financial security. For example, borrowers with a part-time job or overtime income for the past 18 months, but the income cannot be used because the minimum required for a part-time job and/or overtime income is at least a 24-month history. This is verifiable income but cannot be used for income qualification,
Negative Factors Viewed By Mortgage Underwriters
The items below are generally not considered favorable and add to the risk layers of the mortgage loan applicant. Borrowers without their own funds for the down payment and closing costs and no assets. Minimal down payment and 100% gift funds for the down payment and closing costs are considered risk layers. Poor credit history, open collections, numerous charge-offs, history of judgments, tax liens, lack of re-established credit, and recent late payments are considered risk factors.
History of Declining Income Can Be Ground of Mortgage Denial
Declining income year after year. Some lenders will automatically deny borrowers with a history of declining income. This shows instability and the potential that the income will continue to decline for years to come. Short credit history, not enough aged credit tradelines, and limited established credit. High debt-to-income ratios and excessive debt. Multiple jobs and gaps in employment in the past two years are considered risk factors for lenders because it does not show stability.
No verification of rent! In general, mortgage underwriters want to see timely payments in the past 24 months on all manual underwrites. Again, one or two late payments in the past 24 months are not deal killers with strong compensating factors. Underwriters have a lot of underwriter discretion on manual underwrites. Mortgage underwriters can make exceptions on manual underwriting as long as borrowers have strong compensating factors.


March 13, 2022 - 14 min read