Daily Mortgage Interest Rates in Right Now
Mortgage Rates in 2022
Mortgage rates are the interest rates that lenders charge on home loans. They’re an important factor in determining how much house you can afford. The lower the rate, the more monthly payments you’ll make, and the less interest you’ll pay over the life of your loan. Mortgage rates have risen this year, according to many experts, but they’ve done so more quickly than anticipated.
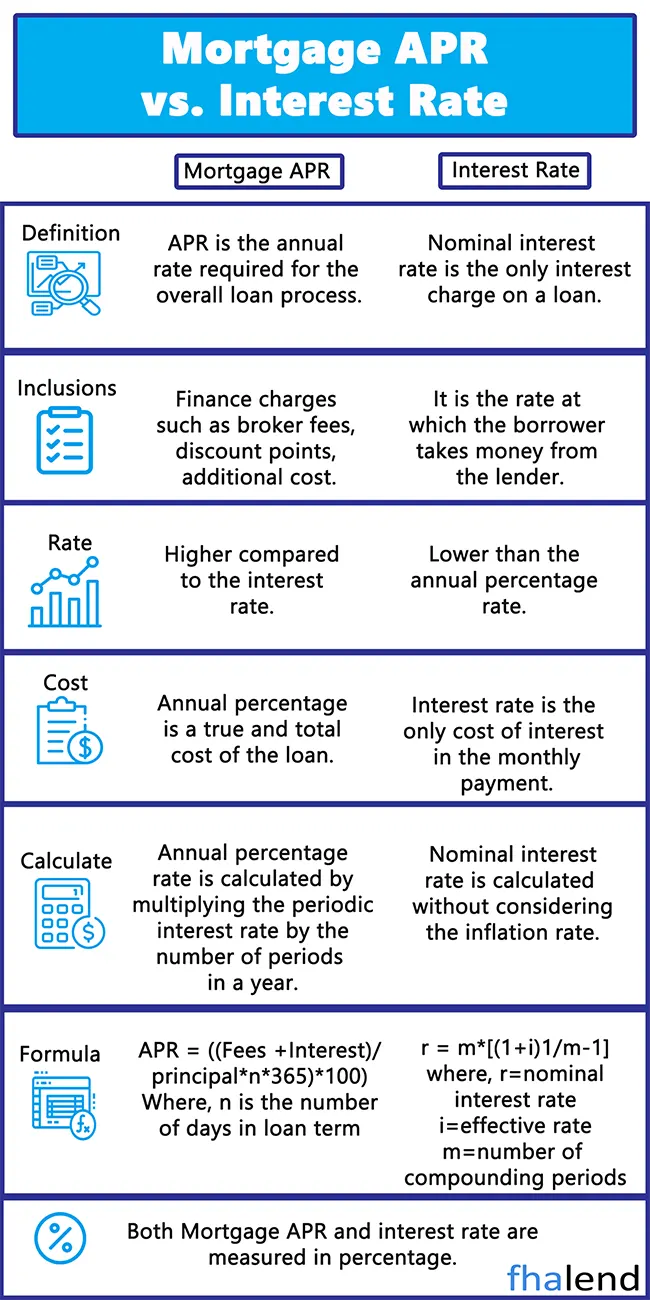
The nominal interest rate, also known as an Annualised Percentage Rate or APR, is the periodic interest rate multiplied by the number of periods per year. For example, a nominal annual interest rate of 12% based on monthly compounding means a 1% interest rate per month (compounded).
Rates on 30-year fixed loans surpassed 5% in April for the first time in more than a decade, driving the cost of mortgages to levels not seen since 2004. While rising interest rates are likely to have a few secondary effects on the housing market, they are unlikely to result in significant house price drops.
There are many factors that can influence mortgage rates, including:
- The health of the overall economy
- Inflationary pressure
- The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy
- Demand/Supply for housing
- And more!
How Mortgage Rates Are Determined?
Mortgage rates are determined by many factors, but there are two main drivers: the health of the overall economy and inflationary pressure. The economy is a key driver of mortgage rates because it impacts the amount of money that lenders are willing to lend. When the economy is strong, lenders feel confident about lending money and they’re more likely to offer competitive rates.
On the other hand, when the economy is weak, lenders may be more cautious about lending money and they’re more likely to charge higher rates. Inflation is another important factor that influences mortgage rates. When inflation is high, it erodes the purchasing power of your dollar and makes it more expensive to borrow money.
 As a result, lenders will typically charge higher rates to offset the effects of inflation. The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy is also a significant driver of mortgage rates. The Fed sets interest rates for short-term loans, which can influence the rates that lenders charge for long-term loans like mortgages.
As a result, lenders will typically charge higher rates to offset the effects of inflation. The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy is also a significant driver of mortgage rates. The Fed sets interest rates for short-term loans, which can influence the rates that lenders charge for long-term loans like mortgages.
When the Fed raises rates, it becomes more expensive for lenders to borrow money, and they’re likely to pass those costs on to borrowers in the form of higher mortgage rates. Finally, demand for housing is another important factor that affects mortgage rates. When there’s high demand for homes, prices tend to go up, and so do mortgage rates. On the other hand, when there’s low demand for homes, prices tend to go down, and mortgage rates usually follow suit.
Why Do Mortgage Rates Matter?
Mortgage rates matter because they have a direct impact on your monthly payments and the total amount of interest you’ll pay over the life of your loan.
The lower your mortgage rate, the lower your monthly payments will be. This can free up more money each month to save or spend on other things. And, over time, you’ll end up paying less in interest because you’re borrowing at a lower rate.
Conversely, the higher your mortgage rate, the higher your monthly payments will be. This can make it more difficult to afford your mortgage payments and can also lead to you paying more in interest over the life of your loan.
Types of Mortgage Rates
Fixed-rate Mortgages
With a fixed-rate mortgage, your interest rate is locked in for the entire term of your mortgage, typically five years. This means that no matter what happens to interest rates during that time, your monthly payments will stay the same.
The biggest advantage of a fixed-rate mortgage is that you’ll always know exactly how much your monthly payments will be, which can make budgeting easier. The downside is that if interest rates go down after you get your mortgage, you’ll be stuck paying the higher rate.
Variable-rate Mortgages
Variable-rate mortgages have an interest rate that fluctuates along with market conditions. This means that your monthly payments can go up or down over time, depending on how interest rates change.
Variable-rate mortgages offer more flexibility since your payments will fluctuate along with interest rates. This means that if rates go down, your payments will go down as well. However, if rates go up, your payments will increase as well. The biggest advantage of a variable-rate mortgage is that you could end up saving money if interest rates go down over the term of your mortgage. The downside is that you could also end up paying more if interest rates go up.
 How Do Mortgage Rates Impact Your Ability to Buy a Home?
How Do Mortgage Rates Impact Your Ability to Buy a Home?
Mortgage rates can have a big impact on your ability to buy a home. When rates are low, it’s easier to qualify for a loan and afford the monthly payments. This is because you can borrow money at a lower rate and stretch your payments out over a longer period of time.
Conversely, when mortgage rates are high, it can be harder to qualify for a loan and afford the monthly payments. This is because you’ll have to borrow money at a higher rate and make your payments over a shorter period of time.
If you’re thinking about buying a home, it’s important to keep an eye on mortgage rates. When rates are low, it’s a good time to buy, but when rates are high, it may be better to wait until they come down.
How to Get The Best Mortgage Rates in 2022?
Get ARM Instead of Fixed Rate in 2022
Pay Points To Lower To Mortgage Rate
Take 30 years instead of 15 years
Don’t Use YSP to Pay For Closings Costs
Ask Seller to Pay Closing Costs
Ask For First Time Home Buyer Program
Ask For a Downpayment Assistance
How to Calculate Principal Balance on Loan
A borrower obtains a loan for $600,000 at 7.5%. If the borrower makes a payment of $4,000 for each month for the next 5 months, what is the principal balance on the 6th month?
The answer is: If the borrower makes a payment of $4,000 each month for the first 5 months, the principal outstanding at the end of that time will be. $600,000[loan] * 7.5%[interest rate] = $45000 [annual interest] % 12 months = $3,750 [interest due].
5 [months] x $250 [$3,750 [principle] – $4,000 [monthly payment]] = $1250 [paid in principal]
$600,000 [total loan amount] – $1250 = $598,750 principles at the 6h month.
How To Calculate Prepaid Interest on a Mortgage
A purchase loan funds on January 23 (January has 31 days). With a loan amount of $550,000 and an interest rate of 7.5% on a 15-year fixed-rate loan, what would be the prepaid interest charged at closing?
The prorated interest is calculated by finding the annual interest, dividing it by the number of days in the year (365), then multiplying that number by the number of days from closing up to the day of the first periodic payment.
In this case: $550,000 [loan amount] x 7.5% [annual interest] = $41,250 [total annual interest]; $41,250 ÷ 365 [days in the year] = $113.01 [daily interest]; $113.01 x 8 [days from closing to the next month] = $904.08 [prepaid interest due]. Some lenders use a 365-day calendar, while others use a 30-day month/360-day calendar. Be aware of the policy used by the lender funding the loan.
Increase Your Downpayment
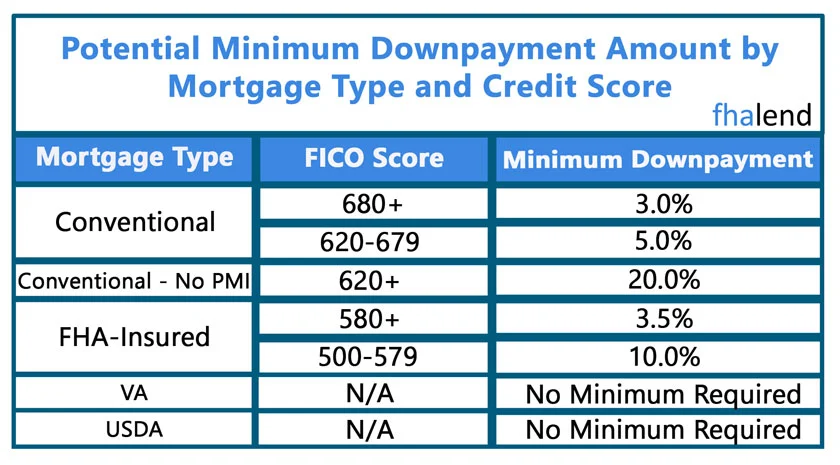
Some veterans and rural borrowers may be eligible for loans that allow 100% financing, requiring no down payment. Other borrowers might qualify for mortgages with down payments as low as 3% or 3.5%. Here’s a rundown of the differences:
- FHA loans – mortgage interest rates are usually higher than other types of loans, but the down payment requirement is much lower. The Federal Housing Administration insures mortgages and allows down payments as low as 3.5 percent. While FHA-insured loans are more forgiving of low credit scores, you will have to pay mortgage insurance for the life of the
- Conventional Loans – some borrowers may qualify for conventional loans that aren’t insured by the government and provide down payments as low as 3%. The majority of mortgages are first-time or low- to moderate-income people. Because you have to pay for private mortgage insurance, or PMI, if your down payment is less than 20% of the home purchase price, these loans have higher interest rates.
- VA loans – If you (or your spouse) are active military or veteran, you might be eligible for a mortgage guaranteed by the Department of Veterans Affairs.
- USDA loans – If you reside in a rural region, the USDA may help cover closing expenses and provide a low- or no-down-payment mortgage.
Mortgage rates matter because they have a direct impact on your monthly payments and the total amount of interest you’ll pay over the life of your loan. When rates are low, it’s a good time to buy a home, but when rates are high, it may be better to wait, or buy and refinance after 6 months if the rates goes back to normal.
Mortgage rates are determined by many factors, including the health of the economy, inflationary pressure, and the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy. They also vary depending on the type of loan you get and the lender you choose.
If you’re thinking about buying a home, it’s important to keep an eye on mortgage rates so that you can time your purchase when rates are most favorable. Working with a knowledgeable loan officer can also help you get the best possible rate on your loan.